Effective **06/17/24** we will be reinstating our no show and cancellation within 24 hours fee. All patients who no show or cancel within 24 hours of their appointment will have a charge of $50 added to their account. This fee does not go to insurance and will be patient responsibility. There will be exceptions for emergent situations.
Cape Fear Family & Med One Care's Business hours are
Monday through Friday 8AM- 5PM
EMG Nerve Conduction
EMG & Testing
Electromyography, or EMG, involves testing the electrical activity of muscles. Often, EMG testing is performed with another test that measures the conducting function of nerves called a nerve conduction study. Because both tests are often performed at the same office visit and by the same personnel, the risks and procedures generally apply to both tests.
Muscular movement involves the action of muscles and nerves and needs an electrical current, which is much weaker than the one in your household wiring.
In some medical conditions, the electrical activity of the muscles or nerves is not normal. Finding and describing these electrical properties in the muscles or nerves may help your primary care doctor diagnose your condition.
EMG may aid with the diagnosis of nerve compression or injury (such as carpal tunnel syndrome), nerve root injury (such as sciatica), and with other problems of the muscles or nerves. Less common medical conditions include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, and muscular dystrophy.
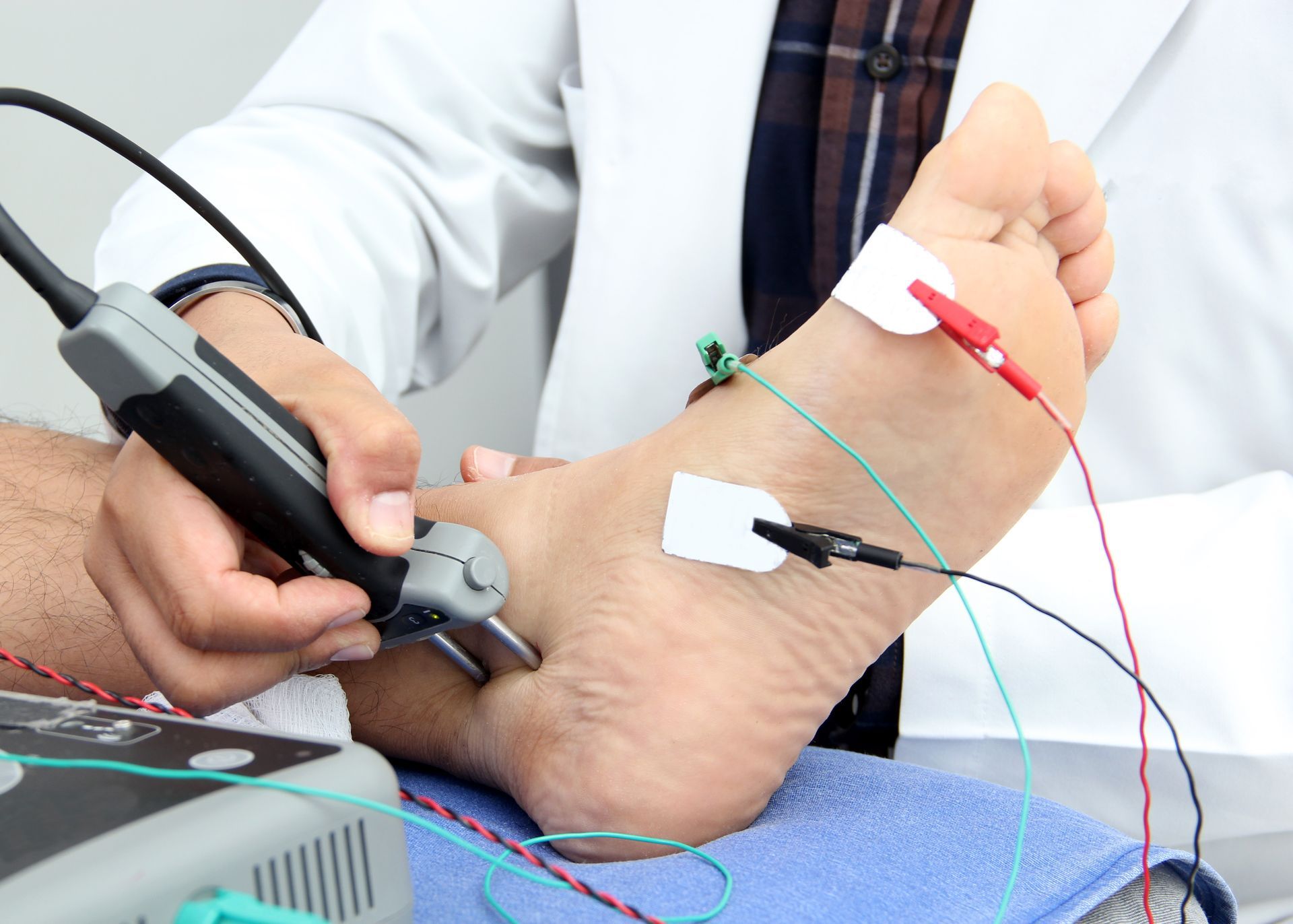
The Procedure
During EMG, small pins or needles are inserted into muscles to measure electrical activity. The needles are different than needles used for injection of medications. The pins are small and solid, unlike hypodermic needles, and since no medication is injected, you will experience less discomfort than with shots.
- You will be asked to contract your muscles by moving a small amount during the testing.
- With nerve conduction studies, small electrodes will be taped to your skin or placed around your fingers. You will typically experience a mild and brief tingling or shock, which may be a bit unpleasant.
- The person who administers the test will explain the procedure. Often muscle activity is monitored through a speaker during the test, which may make a popping or soft roaring noise. The EMG technician will be looking at an oscilloscope, which looks like a small TV set, during the procedure.
- Testing may take 30-60 minutes.
Web Design By | Raven Webworks